Mortgage Insurance is an essential aspect of the homebuying process in Canada, especially for those making a down payment of less than 20%. It plays a critical role in enabling homeownership for many Canadians by allowing lenders to approve high-ratio mortgages. But what many homebuyers don’t realize is that mortgage insurance in Canada primarily protects the lender, not the borrower, in case of loan default. Despite this, it’s the borrower who is responsible for paying the premium, raising the common question: who pays mortgage insurance, and why?
Understanding what is mortgage insurance premium is, how it’s calculated, and who provides it is crucial before you commit to a mortgage. Whether you’re considering private mortgage insurance in Canada through mortgage insurance companies in Ontario, like Canada Guaranty or Sagen, or federally backed options like CMHC, knowing the difference is essential. You might also wonder, “is mortgage insurance tax deductible in Canada?” or “does mortgage insurance go towards principal?” These are important questions every borrower should address.
In this blog, we’ll explain how to calculate mortgage insurance on a conventional loan, who bears the cost, how it fits into your mortgage payments, and ways to reduce or even eliminate mortgage insurance over time. We’ll also discuss borrowers’ mortgage insurance, financed mortgage insurance, and mortgage critical illness insurance — to help you make better-informed decisions on your path to homeownership. Whether you’re a first-time buyer or refinancing, understanding how Canadian mortgage insurance works can save you money and prevent future surprises.
Let’s dive into everything you need to know about mortgage insurance providers in Canada, including costs, conditions, and cancellation options, so you can secure your home with full confidence.
Let’s Understand Mortgage Insurance
Mortgage Insurance in Canada serves a similar purpose to its counterparts in other countries: to protect lenders in the event of borrower default. This insurance provides lenders with the assurance that their investment is safeguarded, enabling them to offer loans to borrowers with lower down payments, typically less than 20% of the home’s purchase price.
Who Pays for Mortgage Insurance?
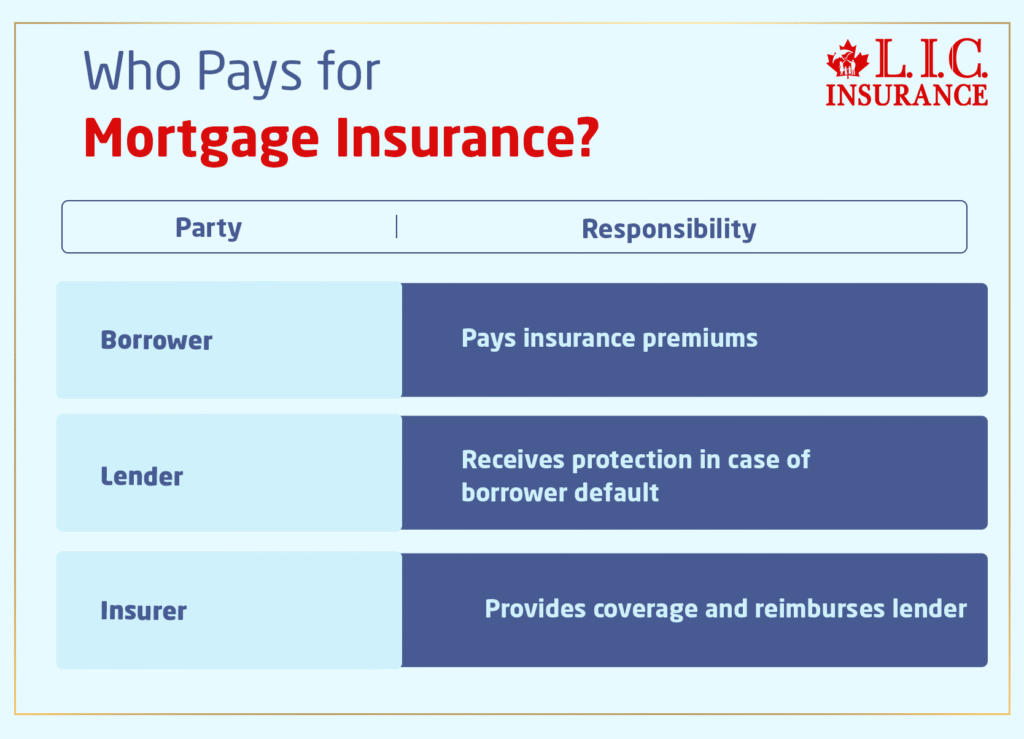
Contrary to common misconceptions, Mortgage Insurance often needs to be clarified among potential home buyers. Here, we break down the complicated dynamics of who shoulders the burden of Mortgage Insurance costs, shedding light on the roles of both borrowers and lenders.
Beneficiary Dynamics:
Mortgage Insurance primarily serves as a safety net for lenders, shielding them from financial risks associated with borrower default.
While lenders reap the benefits of protection, it’s the borrowers who bear the responsibility of funding Mortgage Insurance premiums.
Financial Responsibility:
Borrowers are entrusted with the task of covering the premiums linked with Mortgage Insurance, a commitment integrated into their monthly mortgage payments.
The amount of the down payment, the type of mortgage, and the specific standards set by insurers are just some of the things that affect these premiums, which are kind of like a security fee.
Integration into Monthly Payments:
Mortgage Insurance costs seamlessly meld into borrowers’ monthly mortgage payments, contributing to the overall financial outlay associated with homeownership.
The amalgamation of Mortgage Insurance premiums alongside principal, interest, taxes, and other pertinent expenses facilitates a comprehensive understanding of the financial obligations tied to homeownership.
Variable Premiums:
The fluid nature of Mortgage Insurance premiums renders them subject to variability, influenced by many factors that come naturally to the borrower’s financial profile and the mortgage arrangement.
Getting a Mortgage Insurance quote is one of the most important things that borrowers can do to understand how these premiums work. It gives them useful information about how much the premiums will cost based on their specific situation.
Impacting Factors:
The size of the down payment emerges as a vital determinant, with larger down payments typically correlating with diminished premiums owing to reduced mortgage lender risk.
The type of mortgage, whether conventional or insured through entities like CMHC or private insurers, also influences insurance costs, with insured mortgages often incurring higher premiums due to enhanced mortgage lender protection.
Getting Around Difficulties:
To get around the confusion of Mortgage Insurance, you need to have a deep understanding of how it works financially. This will allow borrowers to make smart choices that are in line with their financial goals.
Borrowers can get useful information about the expected costs, like Mortgage Insurance quotes, which helps them make smart financial decisions and plans.
Types of Mortgage Insurance in Canada
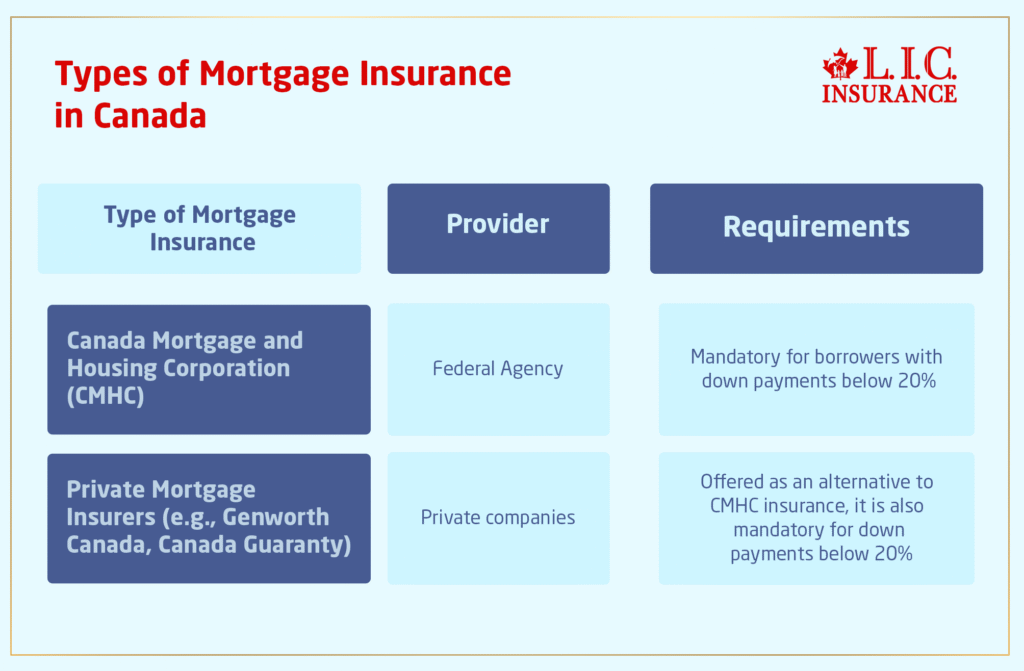
Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC):
- The Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC) is a federal agency responsible for housing policy and Mortgage Insurance in Canada.
- CMHC offers Mortgage Insurance to lenders, providing them with protection against borrower default.
- Borrowers with down payments below 20% are typically required to obtain CMHC Mortgage Insurance, as mandated by federal regulations.
- CMHC insurance enables lenders to extend financing to a wider range of borrowers, including those with smaller down payments.
Private Insurers: Genworth Canada and Canada Guaranty:
- In addition to CMHC, private mortgage insurers such as Genworth Canada and Canada Guaranty also offer Mortgage Insurance in Canada.
- Similar to CMHC insurance, private Mortgage Insurance protects lenders in the event of borrower default, mitigating the risk associated with smaller down payments.
- Private insurers play a vital role in the Canadian mortgage market, offering competitive insurance options to borrowers and lenders alike.
- Borrowers may have the option to choose between CMHC insurance and private insurance, depending on their preferences and lender requirements.
Mandatory Requirement for Borrowers with Down Payments Below 20%:
- Mortgage Insurance is mandatory for borrowers in Canada who make down payments below 20% of the property’s purchase price.
- This requirement is in place to protect lenders against the increased risk associated with smaller down payments.
- By obtaining Mortgage Insurance, borrowers demonstrate their commitment to fulfilling their mortgage obligations, thereby instilling confidence in lenders to extend financing.
Protecting Lenders and Facilitating Homeownership:
- Mortgage Insurance, whether provided by CMHC or private insurers, serves a crucial role in the Canadian housing market.
- By safeguarding lenders against default risk, Mortgage Insurance enables them to offer financing to a broader spectrum of borrowers, including first-time homebuyers and those with limited savings for a down payment.
- Additionally, Mortgage Insurance promotes financial stability by reducing the likelihood of lender losses in the event of borrower default, thus contributing to the overall health of the housing market.
Understanding the various types of Mortgage Insurance available in Canada is essential for prospective homebuyers seeking to explore the complexities of the mortgage process. By familiarizing themselves with options offered by institutions such as Genworth Canada and Canada Guaranty, borrowers can make the right decisions that are in line with their financial goals and circumstances.
In order to explore Mortgage Insurance options tailored to their needs, borrowers are encouraged to consult with reputable insurance experts. By leveraging these resources, borrowers can embark on their homeownership journey with confidence, knowing they have access to comprehensive insurance solutions that can protect both lenders and borrowers.
Remember, Mortgage Insurance is not just a requirement; it’s a way that promotes accessibility to homeownership for many Canadians.
Calculating Mortgage Insurance Costs
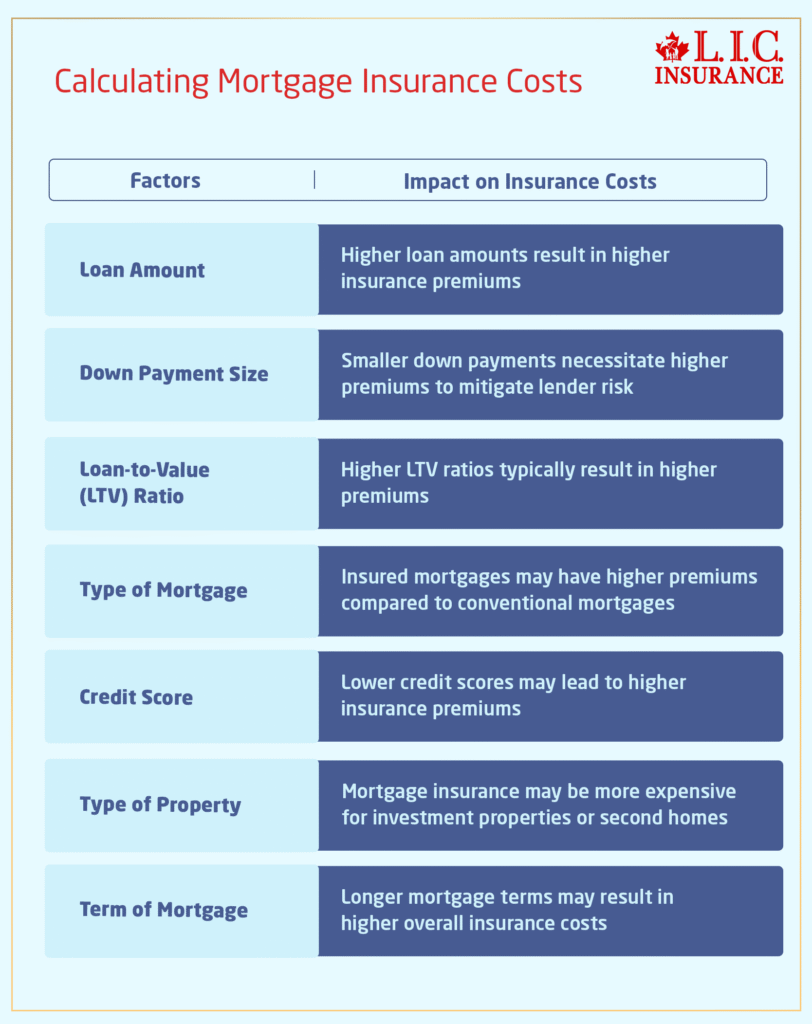
Calculating the costs associated with Mortgage Insurance is an essential step in the homebuying process. To explain this aspect further, let’s break down the factors influencing Mortgage Insurance costs and how borrowers can obtain personalized quotes.
Size of the Down Payment:
The size of your down payment plays a significant role in determining Mortgage Insurance costs. Generally, larger down payments result in lower insurance premiums, as they reduce the lender’s risk.
Loan Amount:
Mortgage Insurance premiums are typically calculated as a percentage of the loan amount. As the loan amount increases, so do the insurance costs. This means that borrowers with larger loan amounts may face higher premiums.
Percentage of the Loan Amount:
Mortgage Insurance premiums are usually expressed as a percentage of the loan amount. This percentage varies depending on factors such as the borrower’s creditworthiness and the type of Mortgage Insurance chosen.
Impact of Down Payment on Premiums:
Smaller down payments often result in higher Mortgage Insurance premiums. This is because a smaller down payment translates to a higher loan-to-value (LTV) ratio, which increases the lender’s risk and, consequently, the cost of insurance.
Obtaining a Mortgage Insurance Quote:
Obtaining a Mortgage Insurance quote is essential for borrowers seeking clarity on Mortgage Insurance costs. Lenders and insurers can provide personalized quotes based on the borrower’s financial profile and the specific details of the mortgage.
Personalized Assessment:
Lenders and insurers consider various factors when providing Mortgage Insurance quotes, including the borrower’s credit score, income, and employment history. By providing accurate information, borrowers can receive a more accurate assessment of their insurance costs.
Transparency and Clarity:
Getting a Mortgage Insurance quote offers transparency and clarity regarding the costs associated with homeownership. It allows borrowers to budget effectively and make the perfect decisions about their mortgage options.
Comparing Quotes:
Borrowers must compare quotes from multiple lenders and insurers to ensure they get the best possible deal. By exploring different options, borrowers can identify cost-effective solutions that fit their financial goals.
Factors Influencing Mortgage Insurance Costs
There are a number of things that affect how much your mortgage protection insurance will cost in Canada. These include:
- Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio: The loan amount in relation to the appraised value of the property or the sales price of the home is a factor when considering what your PMI premium will be. This is a higher premium rate associated with a higher LTV.
- Size of Down Payment: A bigger down payment means the loan-to-value ratio is lower, and that may mean lower Mortgage Insurance rates. On the other side of that, smaller down payments require higher premiums to offset the risk to the lender.
- Mortgage Type: The type of mortgage (conventional vs. insured by CMHC or private insurers) may affect insurance fees. Insured mortgage rates are generally higher because they offer the lender added protection.
A Deeper Look: Overlooked Mortgage Insurance Considerations in Canada
While much is said about who pays mortgage insurance in Canada, there are lesser-known aspects of borrowers’ mortgage insurance that can significantly impact financial planning, especially for those seeking private mortgage insurance in Canada or navigating through mortgage insurance providers in Canada beyond CMHC. One such area is the integration of mortgage critical illness insurance. Unlike standard loan mortgage insurance, this add-on can provide lump-sum payouts to cover your mortgage if you’re diagnosed with a severe illness. It’s not mandatory but it can be life-changing.
A common question among homeowners is: “Is mortgage insurance tax-deductible in Canada?” Generally, the answer is no — mortgage insurance premiums paid on high-ratio mortgages are not tax-deductible in Canada for personal residences. However, in very specific cases involving rental properties, you may be able to claim part of it. Always consult a tax advisor for clarity.
Also misunderstood is “does mortgage insurance go towards principal?” The answer is no. Whether paid upfront or as financed mortgage insurance, it protects the lender, not the homeowner’s equity. Understanding this distinction is crucial when budgeting.
For those wondering how to calculate mortgage insurance on a conventional loan, Canadian mortgage insurance companies in Ontario and beyond generally base it on your loan-to-value ratio (LTV), loan size, and down payment. Lower down payments mean higher mortgage insurance rates in Canada.
Want to know how to eliminate mortgage insurance? In most cases, reaching 20% equity lets you apply for cancellation. Yes — you can cancel mortgage insurance in Canada, especially if you’re with private insurers. This can lead to long-term savings, so it’s worth re-evaluating as your mortgage matures.
For buyers comparing mortgage insurance companies Canada or asking what is mortgage insurance premium exactly, the answer lies in the insurer’s model — CMHC or private — and your financial profile. The Canadian mortgage insurance landscape offers multiple paths, and knowing the right questions can help optimize your strategy.
Wrapping It All Up
In the end, knowing who pays for Mortgage Insurance and how much they will pay is very important for Canadian home buyers. Exploring the pitfalls of mortgage protection insurance can help borrowers make the most informed choices for their fiscal health and history.
Borrowers should consult trusted lenders and insurers to get more insight into the complex Mortgage Insurance world and obtain customized quotes. Those who use these tool can be sound in the knowledge that they actually comprehend what Mortgage Insurance is and what it involves before they begin the process of buying a house.
Keep in mind that Mortgage Insurance is not just an expense – it is a valuable tool that allows many Canadians to achieve home-ownership. Pursue mortgage insurance alternatives that are right for your needs and situation as the first step toward finally buying a home.
Get The Best Insurance Quote From Canadian L.I.C
Call 1 844-542-4678 to speak to our advisors.

FAQs about Mortgage Insurance in Canada
Mortgage Insurance is a policy that protects lenders in case borrowers default on their mortgage payments. It’s necessary for borrowers with down payments below 20% to mitigate the risk for lenders and facilitate access to financing.
Although Mortgage Insurance primarily benefits lenders, borrowers are responsible for paying the insurance premium. These premiums are typically included in the borrower’s monthly mortgage payments.
In Canada, Mortgage Insurance is primarily provided by the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC), as well as private insurers such as Genworth Canada and Canada Guaranty. Depending on their preferences and lender requirements, borrowers may choose between CMHC insurance and private insurance.
Mortgage Insurance works by providing protection to lenders in case borrowers default on their mortgage payments. Borrowers pay insurance premiums, which are included in their monthly mortgage payments. If the borrower defaults, the insurer reimburses the lender for a portion of the outstanding loan amount, reducing the lender’s financial risk.
The Mortgage Insurance premium is typically not tax-deductible in Canada. However, borrowers should consult with a tax professional to understand their individual tax implications related to homeownership and Mortgage Insurance.
Mortgage Insurance covers lenders in case borrowers default on their mortgage payments. If the borrower defaults, the insurer reimburses the lender for a portion of the outstanding loan amount, reducing the lender’s financial risk. Mortgage Insurance essentially compensates lenders for the down payment the borrower didn’t make if foreclosure occurs.
Mortgage Insurance is typically required when borrowers make down payments below 20% of the property’s purchase price. This requirement is mandated by federal regulations and is intended to protect lenders against the increased risk associated with smaller down payments.
No, borrowers with down payments above 20% are not required to have Mortgage Insurance. However, some lenders may still require it as an added precaution.
Mortgage Insurance costs are typically calculated as a percentage of the loan amount. Factors such as the size of the down payment, the type of mortgage, and the insurer’s requirements influence the premiums.
Yes, borrowers can request to cancel Mortgage Insurance once they have accumulated at least 20% equity in their home. This typically involves contacting the lender and providing evidence of the increased equity.
While Mortgage Insurance is a common requirement for borrowers with down payments below 20%, some borrowers may opt for alternative financing options, such as piggyback loans or assistance programs for first-time homebuyers.
Borrowers can obtain a Mortgage Insurance quote by consulting with reputable brokers. These quotes are personalized based on the borrower’s financial profile and the specific details of the mortgage.
If a borrower defaults on their mortgage, the insurer will reimburse the lender for a percentage of the amount owed. However, the borrower remains responsible for any outstanding debt and may face legal consequences for defaulting on the mortgage.
No, Mortgage Insurance premiums are not tax-deductible in Canada. However, borrowers should consult with a tax professional to understand their individual tax implications related to homeownership.
Typically, Mortgage Insurance is not transferable when refinancing a mortgage. If you refinance your mortgage, you may need to obtain new Mortgage Insurance if your loan-to-value ratio exceeds 80%.
Borrowers generally pay for Mortgage Insurance until they reach at least 20% equity in their home. However, the specific duration may vary depending on the type of Mortgage Insurance and lender requirements.
In most cases, borrowers have some flexibility in choosing their Mortgage Insurance provider. However, some lenders may have preferred insurers or specific requirements regarding Mortgage Insurance.
In addition to the insurance premiums, borrowers may incur other fees related to Mortgage Insurance, such as application fees or administrative fees. It’s essential to review the terms and conditions of the Mortgage Insurance policy to understand any additional costs.
Mortgage Insurance typically does not cover job loss or financial hardship. Its primary purpose is to protect lenders in case of borrower default. However, some Mortgage Insurance policies may offer optional coverage for specific circumstances, so borrowers should inquire about available options.
While Mortgage Insurance is typically required until borrowers reach 20% equity, some lenders may allow borrowers to request cancellation earlier under certain conditions. It’s essential to check with the lender or insurer for specific guidelines on cancelling the Mortgage Insurance.
Mortgage Insurance premiums are added to the borrower’s monthly mortgage payments, increasing the total amount due each month. Borrowers should factor in these additional costs when budgeting for homeownership.
Mortgage Insurance itself does not directly impact credit scores. However, failing to pay Mortgage Insurance premiums or defaulting on the mortgage can negatively affect credit scores and overall financial health.
No, Mortgage Insurance is specific to each mortgage loan and property. If you sell your home and buy a new one, you’ll need to obtain new Mortgage Insurance for the new mortgage.
Borrowers can consult with mortgage lenders, insurance providers, or financial advisors to learn more about Mortgage Insurance options and requirements specific to their circumstances. Additionally, government housing agencies such as the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC) provide valuable resources and information on Mortgage Insurance in Canada.
Mortgage Insurance typically does not cover death. Its primary purpose is to protect lenders in case borrowers default on their mortgage payments. However, some Mortgage Insurance policies may offer optional coverage for specific circumstances, such as death or disability. Borrowers should inquire about available options and coverage details with their insurer.
Mortgage Insurance typically stops once borrowers reach at least 20% equity in their home. At this point, borrowers may request to cancel Mortgage Insurance, and it may also automatically terminate as per the lender’s or insurer’s guidelines. Additionally, some Mortgage Insurance policies may have specific termination provisions based on equity milestones or other factors.
The above information is only meant to be informative. It comes from Canadian LIC’s own opinions, which can change at any time. This material is not meant to be financial or legal advice, and it should not be interpreted as such. If someone decides to act on the information on this page, Canadian LIC is not responsible for what happens. Every attempt is made to provide accurate and up-to-date information on Canadian LIC. Some of the terms, conditions, limitations, exclusions, termination, and other parts of the policies mentioned above may not be included, which may be important to the policy choice. For full details, please refer to the actual policy documents. If there is any disagreement, the language in the actual policy documents will be used. All rights reserved.
Please let us know if there is anything that should be updated, removed, or corrected from this article. Send an email to Contact@canadianlic.com or Info@canadianlic.com

